Timeline of Systematic Data and the Development of Computable Knowledge


0

78: Pliny
The world's knowledge, with references
Pliny creates an encyclopedia that claims to summarize all knowledge with references to its sources.

80: Pedanius Dioscorides
Cataloging medicinal substances
Pedanius Dioscorides produces De Materia Medica as a pharmacopeia covering herbal and other medicines.


125: Philo of Byblos
Arranging words
Philo of Byblos compiles a dictionary of synonyms and makes the earliest known thesaurus.
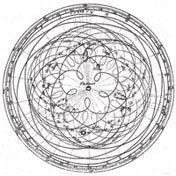
150: Ptolemy
Formulas for the heavens
Ptolemy's Almagest introduces epicycles to describe the detailed motion of planets.
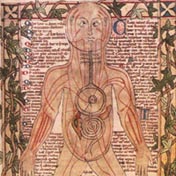
200: Galen
Classifying the body
Galen organizes anatomy and physiology, defining many terms and concepts used today.
500

550: Literary Monasticism
Preserving written knowledge
Cassiodorus founds a monastery devoted to copying, preserving, and translating classic texts, initiating the tradition of literary monasticism.

825: Hindu-Arabic Numerals
Writing numbers using decimal digits
Decimal place-value notation from India appears in Persian mathematician al-Khwarizmi's book on mathematical algorithms.
1000

1086: Domesday Book
William the Conqueror orders a detailed accounting of the land and livestock in England.

1098: Lingua Ignota
Hildegard of Bingen's creation of Lingua Ignota may be considered one of the earliest constructed languages, which used an alphabet of 23 letters.

1230: Hugh of St Cher
Indexing textual knowledge
Hugh of St Cher and a team of 500 other monks create a concordance of The Bible.
1300
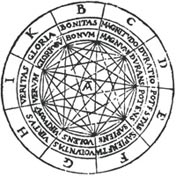
1300: Ramon Llull
Creating knowledge by combinations
Ramon Llull promotes a scheme for systematically creating knowledge from formal combinations of ideas.

1350: Nicole Oresme
Making pictures of data
French philosopher Nicole Oresme introduces the notion of drawing graphs of values.

1403: Yongle
Collecting the knowledge of a civilization
The Yongle Encyclopedia, assembled by 2,000 scholars, fills over 11,000 volumes with the collected knowledge of Chinese civilization.


1450: Vatican Library
The papal archives become the Vatican Library, which is still operating today.

1453: Johannes Gutenberg
Mass distribution of knowledge
Moveable type makes it economical to print many kinds of documents.


1538: Parish Records
Recording life's events
Parishes in England keep weekly records of all christenings, marriages, and burials.

1582: Gregorian Calendar
Pope Gregory XIII establishes the modern calendar, changing the leap year rule for years divisible by 100.
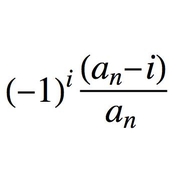
1595: Symbolic algebra
Franciscus Vieta writes mathematical formulas with letters as variables, using vowels for unknowns and consonants for parameters.





